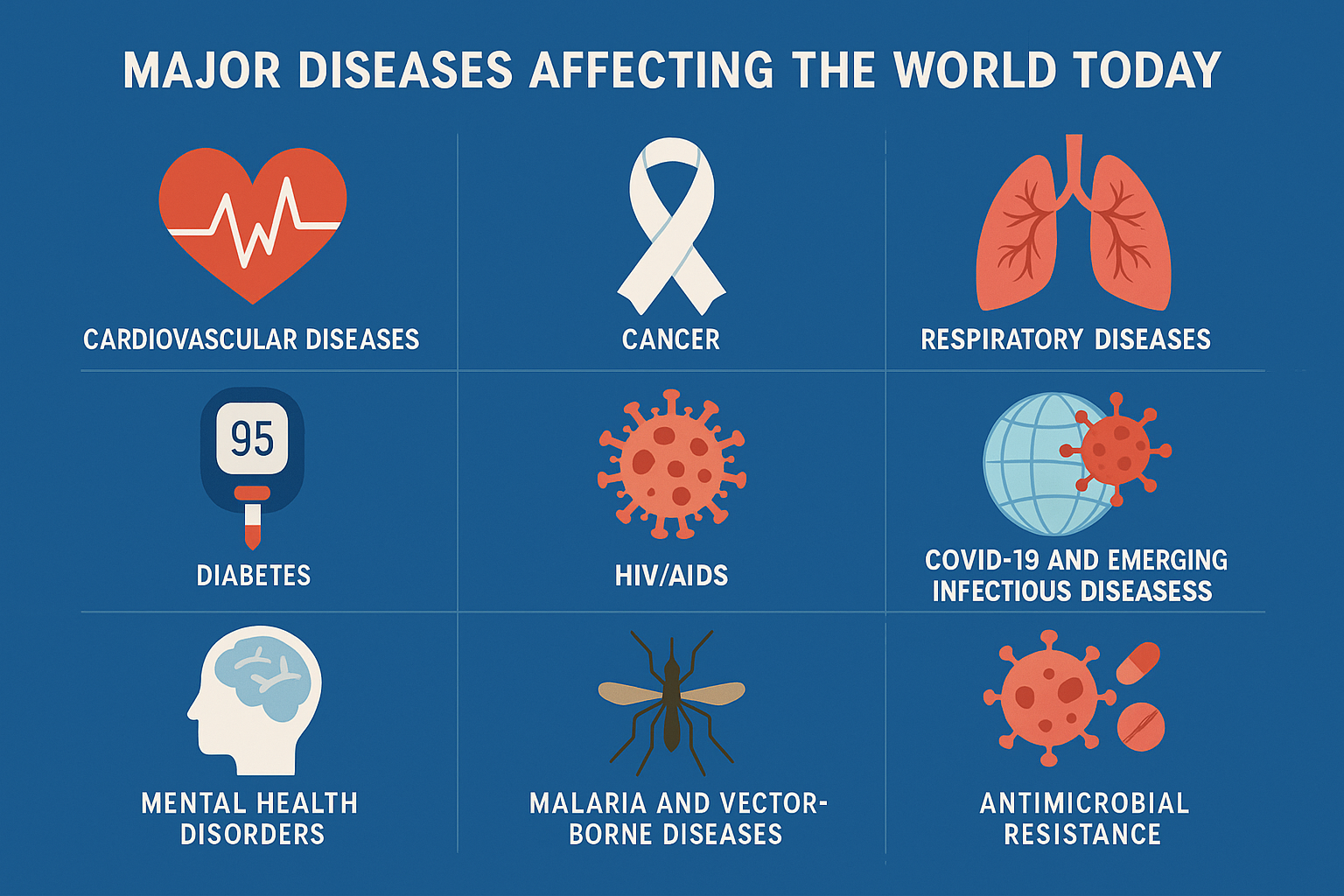
Despite advancements in medicine and public health, several diseases continue to pose significant threats to global well-being. Some are infectious and rapidly spreading, while others are chronic, affecting millions silently over time. This article explores the most pressing diseases of our era, their causes, and what can be done to combat them.
1.
Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs)
📊 Global Impact:
- Leading cause of death globally, responsible for over 17.9 million deaths annually.
- Includes heart disease, stroke, and hypertension.
⚠️ Causes:
- Poor diet (high in saturated fats, sugar, and salt).
- Lack of physical activity.
- Smoking, alcohol use, and stress.
- Genetic predisposition.
✅ Prevention:
- Healthy diet (rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains).
- Regular exercise.
- Routine checkups and blood pressure monitoring.
- Avoiding tobacco and alcohol.
2.
Cancer
📊 Global Impact:
- Over 10 million deaths annually.
- Common types include lung, breast, colorectal, prostate, and cervical cancer.
⚠️ Causes:
- Genetic mutations, smoking, radiation, carcinogens.
- HPV and hepatitis B viruses in some cases.
- Poor lifestyle choices and environmental pollutants.
✅ Prevention and Control:
- Regular screenings (e.g., mammograms, colonoscopies, Pap smears).
- HPV and hepatitis B vaccinations.
- Avoid tobacco, eat antioxidant-rich foods.
- Early detection and timely treatment.
3.
Respiratory Diseases
📊 Global Impact:
- Chronic respiratory diseases like COPD and asthma affect over 300 million people worldwide.
- Infectious ones like tuberculosis and pneumonia also cause millions of deaths.
⚠️ Causes:
- Smoking, air pollution, occupational hazards.
- Infectious agents (bacteria, viruses like influenza, SARS-CoV-2).
✅ Prevention:
- Clean air initiatives, reducing pollution.
- Vaccination (e.g., flu, COVID-19, pneumococcal).
- Smoking cessation.
- Better living conditions and access to healthcare.
4.
Diabetes
📊 Global Impact:
- Over 537 million adults are living with diabetes globally (2021).
- Leads to complications like blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, and amputations.
⚠️ Causes:
- Type 1: Autoimmune.
- Type 2: Poor lifestyle, obesity, age, genetics.
✅ Prevention and Management:
- Healthy eating and regular exercise.
- Monitoring blood sugar levels.
- Medication and insulin management.
- Early diagnosis.
5.
HIV/AIDS
📊 Global Impact:
- Nearly 39 million people living with HIV globally.
- Caused over 40 million deaths since the epidemic began.
⚠️ Causes:
- Unprotected sex, sharing needles, mother-to-child transmission.
✅ Prevention:
- Safe sex practices (use of condoms).
- HIV testing and counseling.
- Antiretroviral therapy (ART).
- Prevention of mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT).
6.
COVID-19 and Emerging Infectious Diseases
📊 Global Impact:
- COVID-19 pandemic caused over 7 million deaths globally since 2020.
- Sparked economic collapse and healthcare system strain.
⚠️ Challenges:
- Rapid mutations and variants.
- Vaccine resistance in some populations.
- Inadequate healthcare access in many regions.
✅ Response:
- Global vaccination programs.
- Rapid diagnostics and surveillance systems.
- Improved pandemic preparedness.
7.
Mental Health Disorders
📊 Global Impact:
- Depression affects over 280 million people worldwide.
- Suicide is a leading cause of death among young people.
⚠️ Causes:
- Genetic predisposition, trauma, stress, social isolation.
- Lack of support systems.
✅ Treatment and Support:
- Therapy and counseling.
- Psychiatric medications.
- Community awareness and stigma reduction.
- Integrating mental health into primary care.
8.
Malaria and Vector-Borne Diseases
📊 Global Impact:
- Malaria alone kills nearly 600,000 people annually, mostly in sub-Saharan Africa.
- Others include dengue, Zika, chikungunya.
⚠️ Causes:
- Mosquitoes (Anopheles, Aedes species).
- Warm, humid climates; poor sanitation.
✅ Prevention:
- Insecticide-treated bed nets.
- Antimalarial drugs and vaccines.
- Vector control programs.
- Public awareness.
9.
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
📊 Global Impact:
- Threatens the effectiveness of antibiotics.
- Could cause 10 million deaths annually by 2050 if unchecked.
⚠️ Causes:
- Overuse and misuse of antibiotics.
- Poor infection control in healthcare settings.
- Lack of new antibiotics.
✅ Steps to Combat:
- Rational antibiotic use.
- Public awareness.
- Development of new drugs.
- Global cooperation.
Key Challenges in Combating These Diseases:
- Inequality in healthcare access.
- Misinformation and vaccine hesitancy.
- Climate change and urbanization.
- Health system overload during pandemics.
- Lack of political will and funding in many regions.
What Needs to Be Done:
🏥 Strengthen Health Systems
- Invest in primary care and infrastructure.
- Train more healthcare workers.
📚 Health Education and Awareness
- Promote early diagnosis and healthy lifestyles.
💉 Preventive Healthcare
- Immunization campaigns.
- Free or subsidized screening programs.
🌐 Global Cooperation
- Sharing data, resources, and vaccine technology.
- Emergency preparedness and response networks.
Conclusion
Global health is at a crossroads. While we have the tools and knowledge to prevent and manage many of today’s major diseases, success hinges on cooperation, education, and commitment at all levels — from individual to international. Tackling these diseases effectively will require a sustained, united effort to build a healthier and more equitable future for all.